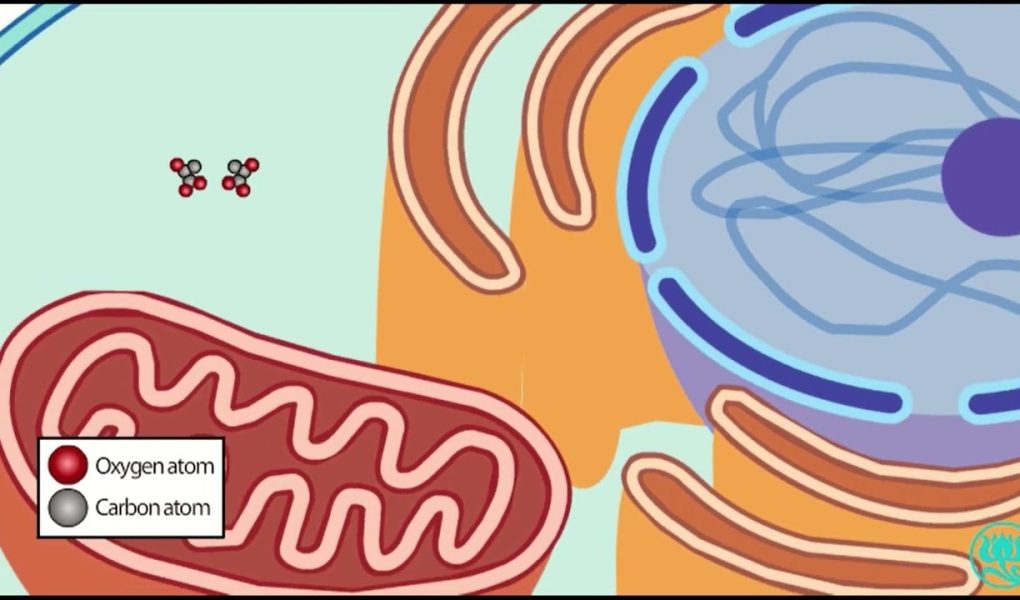
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert glucose and other nutrients into energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This process occurs in all living organisms, from bacteria to humans, and is essential for life.
There are three main stages of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain.
02:18 Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration and takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. It is an anaerobic process, meaning it does not require oxygen. During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon compound. This process also produces two molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADH, a high-energy electron carrier.
06:01 The Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. It is an aerobic process, meaning it requires oxygen. During the citric acid cycle, the two molecules of pyruvate from glycolysis are converted into acetyl-CoA, a two-carbon compound. Acetyl-CoA then enters the citric acid cycle, where it is broken down into carbon dioxide and other molecules. This process also produces two molecules of ATP, eight molecules of NADH, and two molecules of FADH2, another high-energy electron carrier.
11:18 The Electron Transport Chain
The electron transport chain is the final stage of cellular respiration and takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. It is also an aerobic process, requiring oxygen. During the electron transport chain, the high-energy electron carriers NADH and FADH2 from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle are used to generate ATP. The electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed along a series of protein complexes in the inner mitochondrial membrane, creating a proton gradient across the membrane. This gradient is then used by ATP synthase to generate ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
Overall, cellular respiration is a complex and highly regulated process that is essential for the survival of all living organisms. While glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain are the three main stages of cellular respiration, other processes such as oxidative phosphorylation and the proton motive force also play important roles in energy production. Understanding the intricacies of cellular respiration is essential for advancing our understanding of how cells function and for developing new treatments for diseases that affect cellular metabolism.
source