MCQs https://peerr.io/login?refId=drpriya07
Cell Membrane MCQs https://peerr.io/quiz/cell-physiology-cell-biology-eukaryotic-cell-human-cell Watch on 1.5x speed to save time:)
Test your knowledge by solving this quiz!! https://peerr.io/quiz/mitochondria
Read more👉https://decodedmedicine.blogspot.com/2020/06/the-power-house.html
A powerhouse is an installation where energy in the form of electrical power is generated for distribution.
The cells in our body also have energy-producing powerhouses. Each cell contains not just one but many of these powerhouse organelles. The number and size of these organelles vary from cell to cell depending on the cell’s functions. For instance, muscle cells need a lot of energy and have 1000s of them per cell. Whereas each skin cell has just a few 100 of them.
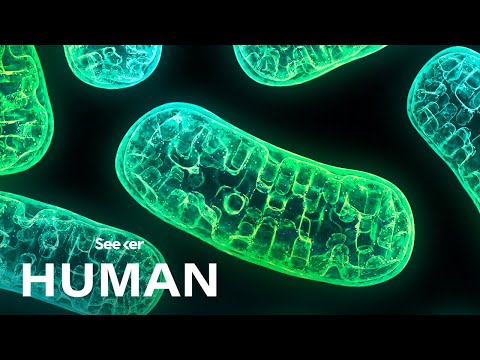
These powerhouse organelles go by the name ‘mitochondria’
Energy is released by the cell’s powerhouse-mitochondria in the form of ATP(adenosine triphosphate). This energy (ATP) is extracted through the metabolism of food by a process called cellular respiration.
The process of cellular respiration consists of four distinct stages, namely (1)Glycolysis (2)Pyruvate oxidation (3)Citric acid cycle, and (4)Oxidative phosphorylation i.e., the electron transport chain
Of these 4 stages, glycolysis occurs in the cell cytoplasm whereas the other 3 stages happen in different areas of the mitochondria of the cell.
In total, 38 molecules of ATP are produced during the whole process of cellular respiration. A majority of this ATP production, 36 to be specific, occurs in the mitochondria of the cell.
Without the mitochondria, cells would be unable to extract energy (ATP) from the nutrients, and all cellular functions would cease.
Structure of the mitochondria & location of enzymes responsible for cellular respiration:
The basic structure of the mitochondrion is composed mainly of two lipid bilayer–protein membranes: an outer membrane and an inner membrane
Many infoldings of the inner membrane form shelves onto which oxidative enzymes are attached.
In addition, the inner cavity of the mitochondrion is filled with a matrix that contains large quantities of dissolved enzymes that are necessary for extracting energy from nutrients.
The enzymes in the matrix operate in association with the oxidative enzymes on the shelves to cause oxidation of the nutrients, thereby forming carbon dioxide and water and at the same time releasing energy in the form of ATP. (click for video explanation)
Timestamps
0:00 Introduction
0:11 Meaning of powerhouse
0;36 What is the powerhouse of the cell?
1:32 Why are the mitochondria called the powerhouse of the cell?
2:51 How are the mitochondria able to function as the powerhouse of the cell?
source