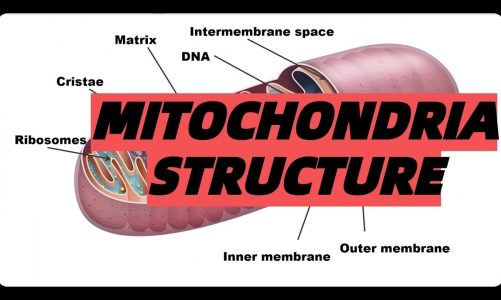
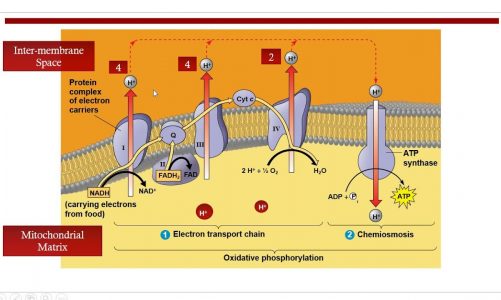
A peroxisome is a type of organelle known as a microbody, found in virtually all eukaryotic cells. They are involved in catabolism of very long chain fatty acids, branched chain fatty acids, D-amino acids, and polyamines, reduction of reactive oxygen species – specifically hydrogen peroxide – and biosynthesis of plasmalogens, i.e., ether phospholipids critical for the normal function of mammalian brains and lungs. They also contain approximately 10% of the total activity of two enzymes in the pentose phosphate pathway, which is important for energy metabolism
A major function of the peroxisome is the breakdown of very long chain fatty acids through beta oxidation. In animal cells, the long fatty acids are converted to medium chain fatty acids, which are subsequently shuttled to mitochondria where they eventually are broken down to carbon dioxide and water. In yeast and plant cells, this process is carried out exclusively in peroxisomes.
source