What Is Electron Transport Chain? | Quick Learn | #shorts #biology #photosynthesis
What Is Dark Reaction/Calvin cycle:
What is photosynthesis?
https://youtube.com/shorts/_YkHXCY5AXA?feature=share
What is light dependent reaction?
What is ATP?
What are chlorophyll a and b?
What Is Chloroplast?
What Is Chlorophyll?
What is NADPH?
What is FADH?
https://youtube.com/shorts/OvsBZI2kTt0?feature=share
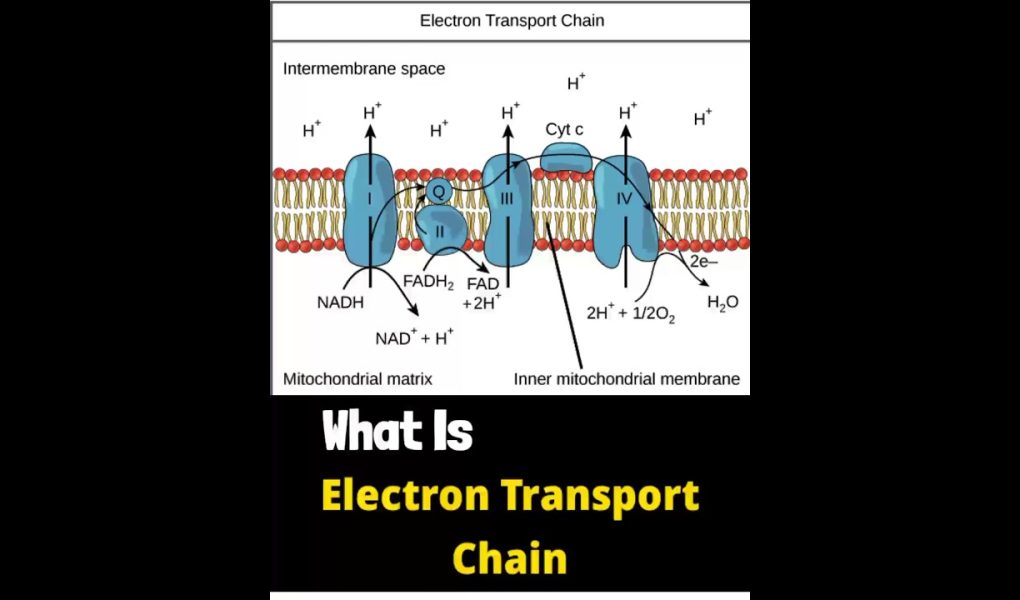
The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and small organic molecules located in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotic cells or in the plasma membrane of prokaryotes. It is responsible for the production of ATP, which is the main source of energy for cellular processes.
During cellular respiration, the ETC accepts high-energy electrons from reduced coenzymes such as NADH and FADH2, and transfers them along a series of electron carriers to oxygen, the final electron acceptor. As electrons are transferred from one carrier to another, energy is released and used to pump protons (H+) across the inner mitochondrial membrane, creating an electrochemical gradient. This gradient is used by ATP synthase to produce ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
The ETC consists of four protein complexes (Complex I, II, III, and IV) and two mobile carriers (ubiquinone and cytochrome c). Each complex contains multiple subunits and cofactors, such as flavin mononucleotide (FMN), iron-sulfur clusters, and heme groups, which allow for the transfer of electrons between carriers.
Overall, the ETC is a critical part of cellular respiration and plays a key role in generating the energy needed for life processes.
The ETC is a process that happens in our cells to produce energy called ATP, which is like the fuel that our body uses to function. The process takes place in the mitochondria, which are like the powerhouses of our cells.
Think of the ETC like a bucket brigade, where people pass buckets of water from one person to another until they reach the end of the line. Instead of buckets of water, the ETC passes electrons, which are like tiny particles of energy.
The ETC has four protein complexes that work together to pass the electrons along. As the electrons move along the chain, they create energy that is used to pump protons (which are like tiny particles) from one side of the mitochondria to the other. This creates a difference in the number of protons on each side of the mitochondria, which is called an electrochemical gradient.
The energy created by the electron transport chain is used by ATP synthase, which is like a tiny machine, to make ATP. ATP is the energy that our body needs to do things like move, breathe, and think.
Overall, the ETC is an important process in our cells that helps us produce the energy we need to live and function.
source