Hello everyone,
Welcome to my channel, Gunjan’s Biology classes!
I hope you are enjoying my videos and if u have any queries or questions or suggestions, kindly comment in the comment box. if u need a ppt of this chapter, mail me at [email protected]
Thank you.
THIS CHAPTER IS DIVIDED INTO 3 PARTS. FOLLOWING ARE THE LINKS OF OTHER 2 PARTS OF THIS CHAPTER and 1 link of important points of this chapter. kindly have a look at them.
This video covers the rest of the cell components i.e. structure and function of mitochondria, plastids, and nucleus.
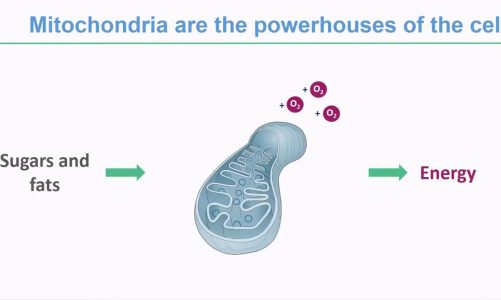
Mitochondria
It has a double membrane structure – The Outer membrane and Inner membrane. The inner membrane is folded to form a structure known as Cristae. It is a site for ATP synthesis. The outer membrane and inner membrane are separated by intermembrane space.
The inner compartment is known as the Matrix. DNA and ribosomes are present in the matrix of the mitochondria.
Plastids
These are found in plant cells. There are three types of plastids- Chloroplast, Chromoplast, and Leucoplast.
Chloroplast contains a green pigment known as Chlorophyll. The leaves appear green due to the presence of chlorophyll in it. The central atom present in chlorophyll is the magnesium ion. Chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis.
The chloroplast is a double membrane structure-inner membrane and outer membrane. The space limited by the inner membrane of the chloroplast is called the stroma. The stroma contains a flattened sac-like structure known as Thylakoids.
It is the site of photosynthesis. Thylakoids are stacked upon each other to form grana. Each granum is connected with another granum by a lamella. Similar to mitochondria, chloroplast contain DNA and ribosomes.
Chromoplast provides color to flowers and fruits. The pigment present in chromoplast is carotene which provides red color and xanthophyll which provides the yellow-orange color.
Leucoplast is of different types such as amyloplast for storage of starch, aleuroplast store proteins and elaioplast stores oil and fats.
Nucleus
It is a double membrane structure. The outer membrane is continuous with the ER and contains ribosomes on it. The space between the two membranes is known as Perinuclear Space. The two nuclear membranes are interrupted by minute pores known as Nuclear Pores, which allow only certain molecules of a particular size to enter the nucleus. The nuclear matrix is known as Nucleoplasm.
Nucleoplasm is composed of chromatin and nucleolus.
source